Serial Data Busses
The databus is able to communicate with other devices through a data bus. A data bus is a system that allows two or more devices (such as sensors and microcontrollers) to communicate in a well defined manner. This allows an efficient and interoperable way of data transfer between those devices.
On such a bus the data-bytes are encoded into fast electrical pulses and transmitted using one or more wires. There are many different data buses in use (eg. I²C and OneWire), which differ in the amount of wires, connectable devices, and their bandwith.
The I²C-Protocol
Most of our sensors transfer their data via the I²C bus.
This bus is an easy to use data bus which may connect many devices to a master device.
It utilizes two wires to transmit the data; SDA (serial data) and SCL (serial clock).
The SDA wire transmits the actual data bytes, while a timing signal is sent on the SCL wire to keep all devices in sync.
Our Arduino Uno has dedicated pins for this bus on A4 (SDA) and A5 (SDC).
If we want to connect more than one device to the Arduino, we create interconnect them on a serial circuit: The two wires can be passed on from each slave device to the next.
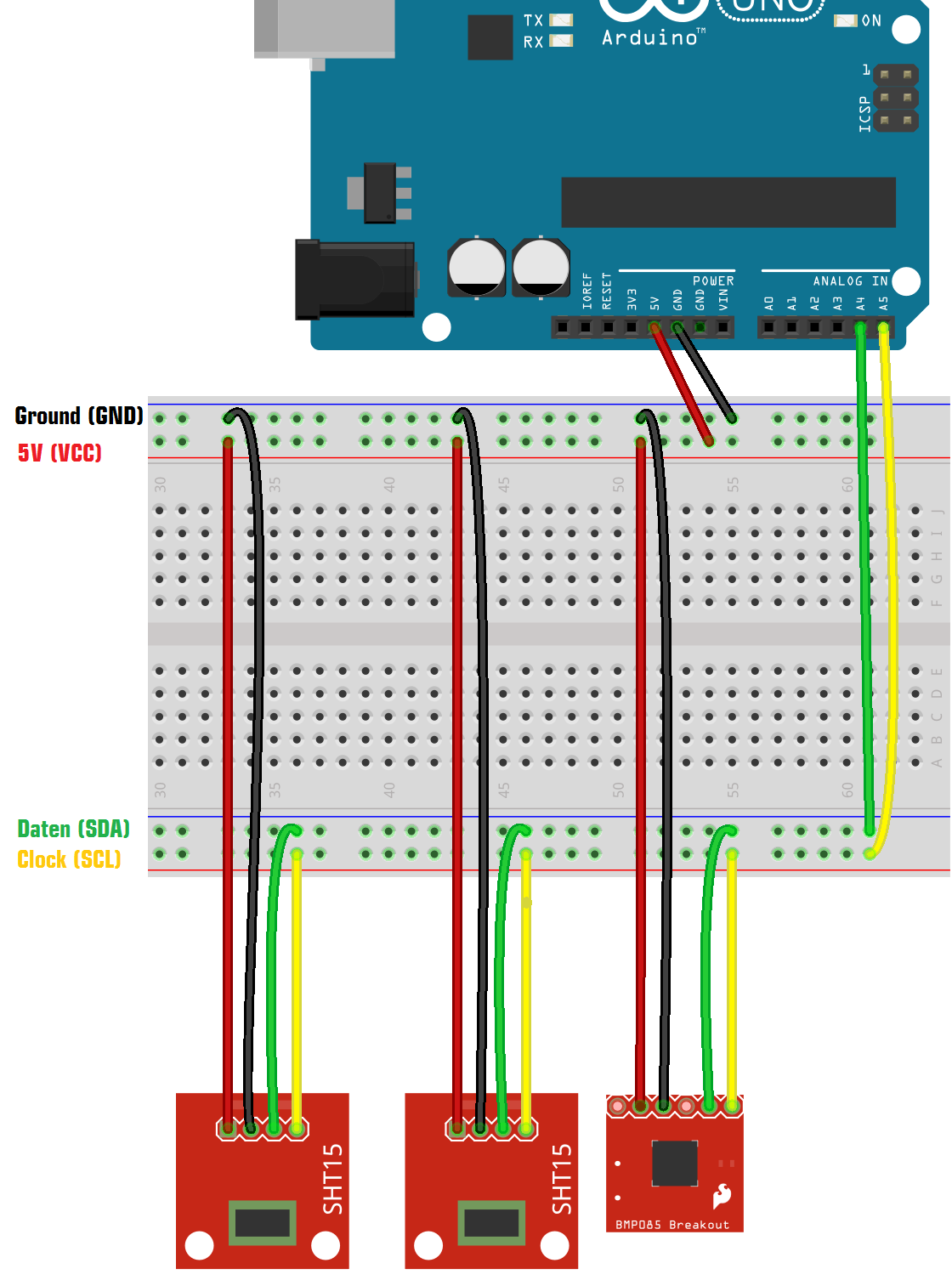
When using the I²C bus, the Arduino always is the master device, and all other devices slave. Each slave has an hexadecimal address, which is used to uniquely identify the device on the bus when communicating with it. Usually these address is hardcoded in the device, and can be looked up in the device's datasheet.
The Wire.h Library
To be able to communicate on the I²C bus, we have to use the Wire library.
It is included with the Arduino IDE, and has to be included in your sketch with the following line at the top of the sketch:
#include <Wire.h>
Data is transmitted byte by byte. To send a byte, three commands have to be called:
Wire.beginTransmission(ADDRESS);This command initializes the communication.
ADDRESSis the corresponding address of the device, eg.0x76.Wire.write(DATA);Send a byte
DATAto the previously connected device. To send multiple bytes, call this function several times.Wire.endTransmission();Closes the connection again.
For the transmission in the other direction - ie. recieving data - we use the following 4 commands:
Wire.beginTransmission(ADDRESS);Wire.requestFrom(ADDRESS, NUM_BYTES);Request
NUM_BYTESto be transmitted to us from the device identified byADDRESS.char incoming = Wire.read();Read one requested byte. Call
NUM_BYTEStimes to recieve all data.Wire.endTransmission();
